All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Annuities supply tax-deferred development. When you earn rate of interest in an annuity, you typically don't need to report those earnings and pay revenue tax obligation on the earnings yearly. You can maintain funds in your account to reinvest and intensify. Growth in your annuity is protected from personal revenue tax obligations. Eventually, you will have to pay earnings taxes on withdrawals from an annuity agreement.
While this is a review of annuity taxes, get in touch with a tax obligation specialist prior to you make any kind of decisions. Annuity income stream. When you have an annuity, there are a variety of information that can impact the tax of withdrawals and income settlements you receive. If you put pre-tax cash right into an individual retired life account (IRA) or 401(k), you pay taxes on withdrawals, and this holds true if you fund an annuity with pre-tax cash
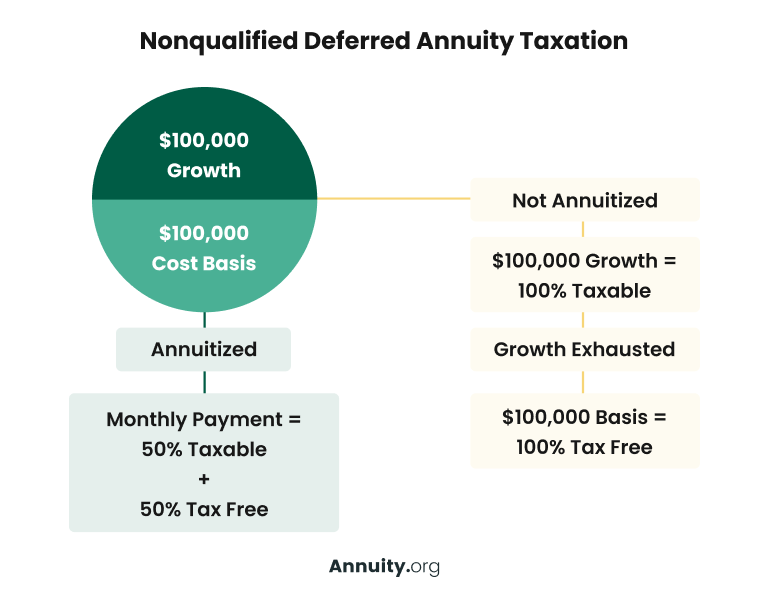
If you contend least $10,000 of earnings in your annuity, the whole $10,000 is treated as income, and would generally be tired as regular earnings. After you tire the profits in your account, you get a tax-free return of your initial round figure. If you convert your funds into an assured stream of income payments by annuitizing, those settlements are divided into taxed parts and tax-free portions.
Each payment returns a part of the cash that has actually already been strained and a section of passion, which is taxed. For instance, if you receive $1,000 per month, $800 of each payment may be tax-free, while the continuing to be $200 is gross income. Ultimately, if you outlive your statistically figured out life span, the whole amount of each repayment could come to be taxed.
Given that the annuity would certainly have been funded with after-tax money, you would certainly not owe taxes on this when withdrawn. Since it is categorized as a Roth, you can also possibly make tax-free withdrawals of the growth from your account. To do so, you should comply with several IRS regulations. As a whole, you must wait up until at the very least age 59 1/2 to withdraw incomes from your account, and your Roth has to be open for at least five years.

Still, the other functions of an annuity may outweigh revenue tax therapy. Annuities can be devices for deferring and managing taxes. Examine just how best to structure your retired life, philanthropic offering and other monetary objectives with the assistance of a monetary specialist and tax obligation expert. A tax-aware technique could assist you take advantage of annuity advantages and prevent surprises in the future.
Are Retirement Annuities taxable when inherited
If there are any penalties for underreporting the income, you could be able to ask for a waiver of fines, yet the rate of interest generally can not be waived. You could be able to prepare a layaway plan with the internal revenue service (Annuity income riders). As Critter-3 stated, a local expert could be able to help with this, yet that would likely lead to a little added expense

The original annuity contract owner should include a fatality advantage stipulation and call a beneficiary - Period certain annuities. There are different tax obligation repercussions for partners vs non-spouse beneficiaries. Any beneficiary can choose to take an one-time lump-sum payment, however, this includes a hefty tax burden. Annuity recipients are not restricted to people.
Fixed-Period Annuity A fixed-period, or period-certain, annuity makes sure payments to you for a certain size of time. Life Annuity As the name suggests, a life annuity warranties you payments for the remainder of your life.
Are Annuity Cash Value taxable when inherited
If your contract includes a fatality benefit, continuing to be annuity payments are paid out to your beneficiary in either a lump sum or a series of repayments. You can select someone to obtain all the available funds or several people to get a percentage of continuing to be funds. You can also choose a nonprofit company as your recipient, or a trust developed as part of your estate strategy.
Doing so allows you to maintain the exact same choices as the original owner, including the annuity's tax-deferred standing. You will certainly also have the ability to get staying funds as a stream of repayments rather than a round figure. Non-spouses can likewise inherit annuity payments. However, they can not transform the terms of the contract and will only have accessibility to the marked funds laid out in the initial annuity contract.
There are 3 primary ways beneficiaries can receive inherited annuity settlements. Lump-Sum Circulation A lump-sum distribution allows the recipient to obtain the contract's entire staying value as a solitary repayment. Nonqualified-Stretch Arrangement This annuity contract provision allows a recipient to obtain repayments for the rest of his/her life.
Any kind of beneficiary including partners can choose to take a single round figure payout. In this instance, taxes are owed on the whole difference between what the initial proprietor paid for the annuity and the death benefit. The swelling amount is tired at normal earnings tax obligation prices. Round figure payments lug the highest possible tax problem.
Spreading out payments out over a longer time period is one way to avoid a large tax obligation bite. As an example, if you make withdrawals over a five-year duration, you will owe tax obligations only on the raised value of the part that is withdrawn in that year. It is additionally much less likely to press you right into a much greater tax obligation bracket.
Tax consequences of inheriting a Lifetime Annuities
This uses the least tax exposure but likewise takes the lengthiest time to get all the cash. Annuity income stream. If you've acquired an annuity, you frequently must choose about your fatality advantage quickly. Choices concerning just how you desire to obtain the cash are often final and can not be altered later on
An acquired annuity is a monetary item that enables the recipient of an annuity agreement to continue getting payments after the annuitant's death. Acquired annuities are frequently made use of to give earnings for loved ones after the fatality of the key breadwinner in a household. There are two sorts of inherited annuities: Immediate inherited annuities begin paying out immediately.
Are inherited Flexible Premium Annuities taxable income
Deferred inherited annuities permit the recipient to wait till a later day to start receiving repayments. The most effective thing to do with an acquired annuity depends on your monetary circumstance and requirements. An instant inherited annuity may be the ideal alternative if you require instant earnings. On the other hand, if you can wait a while prior to starting to receive repayments, a deferred inherited annuity may be a far better choice. Annuity interest rates.
It is very important to talk with a monetary advisor prior to making any type of choices concerning an acquired annuity, as they can help you determine what is finest for your private conditions. There are a couple of threats to take into consideration prior to buying an inherited annuity. You ought to recognize that the federal government does not assure inherited annuities like other retirement items.
Inherited Fixed Annuities taxation rules
Second, inherited annuities are frequently complex monetary products, making them difficult to recognize. Consulting with a financial expert prior to buying an inherited annuity is very important to ensure you fully recognize the risks included. There is constantly the risk that the value of the annuity can go down, which would lower the quantity of money you get in payments.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Exploring the Basics of Retirement Options Key Insights on Your Financial Future Breaking Down the Basics of Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Retirement Plan
Understanding Financial Strategies Everything You Need to Know About Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pros And Cons Defining the Right Financial Strategy Features of Fixed Vs Variable Annuities Why Fixed Inc
Exploring the Basics of Retirement Options Everything You Need to Know About Variable Annuities Vs Fixed Annuities Defining Variable Annuities Vs Fixed Annuities Pros and Cons of Fixed Income Annuity
More
Latest Posts